What is PLC ?
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) focuses on automating different electro-mechanical processes taking place in various industries. With a well-programmed microprocessor, It has specially designed and implemented controllers which are immune to extremely high and low temperatures, humidity, dust, etc.
Just like any usual program, the coding is programmed on a computer. From here it is transferred to the PLC using a cable. After downloading the programs, these are loaded and stored in the PLC. In order to make sure the programs do not vanish at the time of power cut or switch off, it uses non-volatile memory storage.
It is programmed using a programming language called Ladder Logic. It is already known that it is an industrial computer. In order to program it, a programming language had to be designed in such a way, that the electricians and electrical engineer in an industry could easily understand and feel comfortable enough to code in it.
A Programmable Logic Controller consists of various input and output terminals. Using the input terminals, it interprets the logical states from switches and sensors. There are two logical states also known as high(or 1) and low(or 0). The output from the output terminals is used as a signal for various devices, providing them on/off controls. The electrical engineers understand the ladder logic diagrams and so it was the inspiration behind the programming language used to program its.
The most commons areas of use are in a washing machine, elevators and also traffic signals.
Definition:-
Programmable Logic Controller, more popularly known as PLC is a digital computer without a mouse or a keyboard or a monitor.
Or
A Programmable Logic Controller, or PLC, is a ruggedized computer used for industrial automation. These controllers can automate a specific process, machine function, or even an entire production line
Understanding PLC:-
Programmable Logic Controller is a small computer which automatically controls various processes and components in an industrial system. For the sake of comparison, let’s take a process that is manual as an example thinks of PLC as a brain controlling a finger on a trigger of an applicator. The brain sends a signal to the finger directing it to pull the finger when something is dispensed and when the brain wants to stop it sends another signal. Like most of the brains, it can multitask and it’s lightning fast Just like that, it can control much input and output signal like direct a paint line to change colors so all the widgets being painted go from one color to other.
Working:-
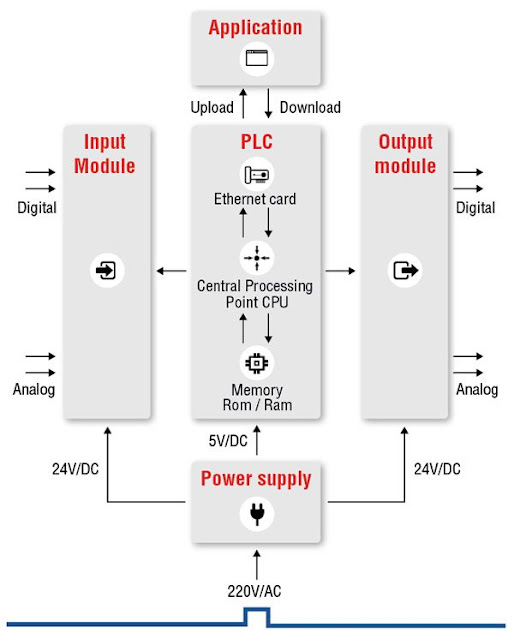
It communicates to the CPU status of the field devices as well as acts as a tool to control. The programming device is actually a computer loaded with programming software which will allow a user to create and make changes in the PLC software. The memory provides storage media for the PLC program as well as for other data.
How does a PLC work?
The PLC receives information from connected sensors or input
devices, processes the data, and triggers outputs based on pre-programmed
parameters.
Depending on the inputs and outputs, a PLC can monitor and record run-time data
such as machine productivity or operating temperature, automatically start and
stop processes, generate alarms if a machine malfunctions, and more.
Programmable Logic Controllers are a flexible and robust control solution,
adaptable to almost any application.
• I/O – The PLC’s CPU stores and processes program data, but input and output modules connect the PLC to the rest of the machine; these I/O modules are what provide information to the CPU and trigger specific results. I/O can be either analog or digital; input devices might include sensors, switches, and meters, while outputs might include relays, lights, valves, and drives. Users can mix and match a PLC’s I/O in order to get the right configuration for their application.
• Communications – In addition to input and output devices, a PLC might also
need to connect with other kinds of systems; for example, users might want to
export application data recorded by the PLC to a supervisory control and data
acquisition (SCADA) system, which monitors multiple connected devices. PLCs
offer a range of ports and communication protocols to ensure that the PLC can
communicate with these other systems.
• HMI – In order to interact with the PLC in real time, users need an HMI, or
Human Machine Interface. These operator interfaces can be simple displays, with
a text-readout and keypad, or large touchscreen panels more similar to consumer
electronics, but either way, they enable users to review and input information
to the PLC in real time.
Advantages:-
- Easily programmable
- Well shielded to outlast harsh situations
- Input and output interface available where thousands of input and output can be controlled through a single PLC
- Highly reliable
- Easy to maintain
Required skills:-
PLC professionals are experts in concepts, electrical designs. They are also knowledgeable about fabrication and circuit board layout.
Also, they entail meeting with global standards in providing solutions to companies. This ensures making tasks easier by correct relaying of messages and the required team coordination.
Why should we use PLC?
The most common use of it is in washing machines, controlling traffic signals, elevators, etc. Also, we cannot neglect the use of PLCs in industries to monitor and control building systems and production processes.
Why do we need PLC and What can you do with PLC?
It is needed to automate machines in the industry so that human efforts can be reduced thus minimizing the human errors that might occur in the process. Consider a situation where a human handling a system missed to switched the motor on. Imagine the delay it might cause in the operation to begin. The simple solution to solve this is by automating the motor using PLC. So the basic and most important use of it is in the automation of machines.
Who is the right Audience for learning PLC Technologies?
The one-step solution to learning is various available courses online. It is also the best economical and easy way, however, the challenge in learning PLC online is you might learn the names and functioning of software and hardware parts of PLC, the ladder logic diagrams creation or configuring the various modules but just the theoretical knowledge is not enough. In order to be successful, one needs to have a hands-on experience. The one with an interest and background in logic diagrams and controls can start with the PLC programming tool. An elaborate program for an application is not at all an easy task to create. You need a lot of practice and hands-on to do so. In order to excel in this, one can begin from a small machine building company to gain insight and full-fledged skills and experience of the job.
Scope and How this Technology will help you in Career Growth?
As we all know that every industry is moving on to automating its processes and tools, the demand for the programmer is rapidly increasing. Industrial sectors in India like food and beverages, manufacturing industry, oil and gas industry, transport, process industries, etc are also stepping into Industrial Automation. As a matter of fact, technologies like AI, IOT are merging with OT or operational technologies which includes PLC, SCADA, DCS. Renowned companies like SIEMENS, Mitsubishi, Fanuc, Honeywell, etc provide their product and services all over the world. One can find many opportunities in IT and OT sectors as developer, testers, an analyst for it and so we can say that there awaits a bright successful future in automation for the same.
Conclusion
These applications are specifically highly customized systems. It is cheaper when compared to the price of a specific custom-built controller. Generally, it requires less maintenance and is more robust, henceforth making the things they control work better, despite the environment.




No comments:
Post a Comment